Organoid quantification of droplet microarrays
- Contact:
Marcel Schilling
- Project Group:
Machine Learning for High-Throughput Methods and Mechatronics (ML4HOME)
- Funding:
KIT Future Fields II
- Partner:
IBCS-FMT (Group Levkin)
- Startdate:
01.01.2021
Cancer as a disease is the second leading cause of death worldwide. Tough, cancer treatment is hampered by the development of resistance to current therapies. Combining the multi-omics data of individual tumors with the information about their in-vitro Drug Sensitivity and Resistance Test (DSRT) can help determine a suitable therapy for each patient. Miniaturized high-throughput technology such as droplet microarray enables personalized oncology.
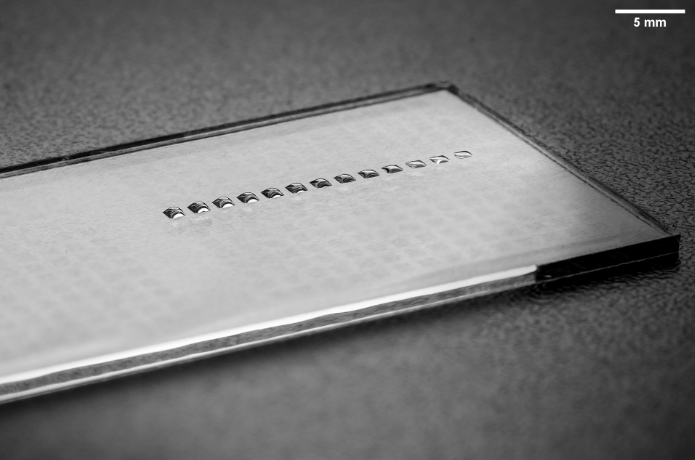

The project focus on the development of a platform including workflows for DSRT profiling from minute amount of cellular material and reagents. Experimental results often rely on microscopy-based fluorescence readouts techniques. However, manual image analysis is time-consuming, not reproducing, and in case of high-throughput not even possible due to the amount of data generated. Therefore, automated image processing solutions are an essential component of a screening platform for personalized oncology.
The goal of the IAI work packages is to develop workflows, algorithms, and interfaces using deep learning for automated high-throughput image processing.
Tools:
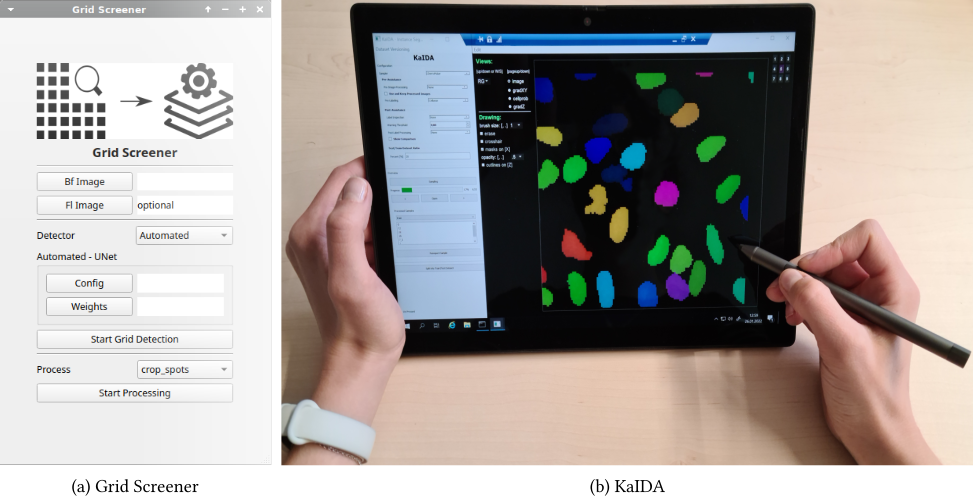
- Grid Screener
- Karlsruhe Image Data Annotation Tool (KaIDA)
Publications
Neumann, O.; Schilling, M.; Reischl, M.; Mikut, R.
2022. Proceedings - 32. Workshop Computational Intelligence: Berlin, 1. - 2. Dezember 2022. Hrsg.: H. Schulte; F. Hoffmann; R. Mikut, 11–30, KIT Scientific Publishing
Rettenberger, L.; Schilling, M.; Reischl, M.
2022. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering, 8 (2), 329–332. doi:10.1515/cdbme-2022-1084
Schilling, M. P.; Ahuja, N.; Rettenberger, L.; Scherr, T.; Reischl, M.
2022. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering, 8 (2), 197–200. doi:10.1515/cdbme-2022-1051
Schilling, M. P.; Schmelzer, S.; Klinger, L.; Reischl, M.
2022. Journal of Integrative Bioinformatics, 19 (4), Art.-Nr.: 20220018. doi:10.1515/jib-2022-0018
Chakraborty, S.; Luchena, C.; Elton, J. J.; Schilling, M. P.; Reischl, M.; Roux, M.; Levkin, P. A.; Popova, A. A.
2022. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 11 (12), Art.-Nr.: 2102493. doi:10.1002/adhm.202102493
Schilling, M. P.; Scherr, T.; Munke, F. R.; Neumann, O.; Schutera, M.; Mikut, R.; Reischl, M.
2022. IEEE access, 10, 2753–2765. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3140378
Schilling, M. P.; Schmelzer, S.; Gómez, J. E. U.; Popova, A. A.; Levkin, P. A.; Reischl, M.
2021. IEEE access, 9, 166027–166038. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3135709
Schilling, M. P.; Rettenberger, L.; Münke, F.; Cui, H.; Popova, A. A.; Levkin, P. A.; Mikut, R.; Reischl, M.
2021, November 26. 31. Workshop Computational Intelligence (2021), Berlin, Germany, November 25–26, 2021
Schilling, M. P.; Rettenberger, L.; Münke, F.; Cui, H.; Popova, A. A.; Levkin, P. A.; Mikut, R.; Reischl, M.
2021. Proceedings - 31. Workshop Computational Intelligence : Berlin, 25. - 26. November 2021. Hrsg.: H. Schulte; F. Hoffmann; R. Mikut, 211–234, KIT Scientific Publishing
Schilling, M. P.; Neumann, O.; Scherr, T.; Cui, H.; Popova, A. A.; Levkin, P. A.; Götz, M.; Reischl, M.
2021, November 8. 7th bwHPC Symposium (2021), Online, November 8, 2021

